Mevas is using a 60-point checklist for material handler inspections
- Basic Machine information and configuration
- Operator Station details and condition
- Engine condition and operation
- Condition of Exterior (frames, boom, sheet metal, paint)
- Visual condition of the Power Train (axles, gearbox, transmission, differentials)
- Condition of the Hydraulic system (hoses, cylinders, pumps)
- Functional test
- Condition of the attachment
- Comments and recommendation for repairs
- Transport dimensions
See a sample of a report below. The picture shows an obsolete version. With a Mevas inspection you would receive the latest version of our checklist.
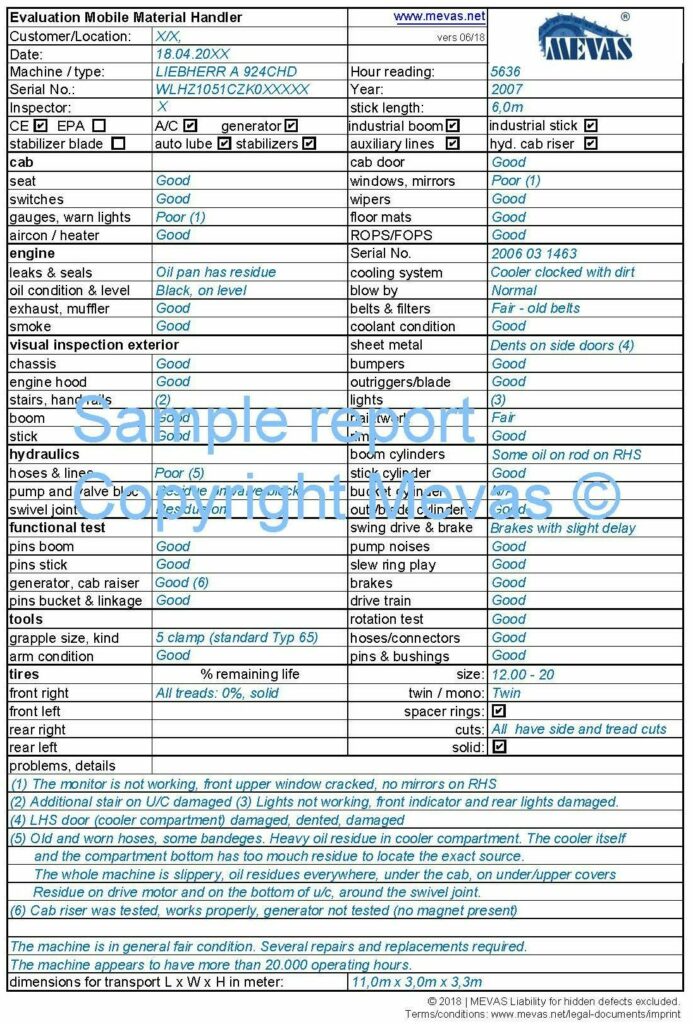
What extras can you order?
Once you receive an offer it will be always for a basic walk-around with functional check. This level is called TA1. On our Checklist-Options page you can find additional services which you can order.
If you have questions about the service please contact the team by Whatsapp or by phone +493520639150. We are happy to answer in detail.
Pictures and video coming with a Mevas-Report
Each machine inspection comes along with 50-80 pictures and in some cases with a short video. In case of interest it is possible to see a material handler report in detail on our Google-Drive folder.

Video about a Material handling inspection by Mevas
For some kind of machines we made a video about the inspection process. For a mobile material handler inspection a short video is available on our YouTube-Channel.
Other sample reports heavy machinery
Visit our overview for other sample inspection checklists for heavy machinery.
Keep in mind: Report forms are our legal property and copying is a violation of our copyright.
Important items to check during Material handler inspection
- Visual inspection
- Inspect the overall condition of the material handler for signs of wear, damage or corrosion.
- Check for any loose or missing bolts.
- Examine the structure, including the boom, frame and any attachments, for cracks or deformities.
2. Hydraulic system
- Check hydraulic hoses and connections for leaks or damage.
- Inspect cylinders for signs of leaks, damage, or improper operation.
- Ensure proper hydraulic fluid levels and look for contamination.
3. Electric
- Inspect the electrical wiring for damage or loose connections.
- Check the battery for proper voltage and secure connections.
- Test all controls and switches for proper functionality.
4. Tires
Inspect tires for wear, damage and proper inflation. Material Handler tires often have gouges.
5. Brakes
- Test the brakes for responsiveness and effectiveness.
- Check automatic axle blocking on turn of superstructure.
- Check the park brake funtion.
6. Cab
- Ensure that the operator’s seat is secure and in good condition.
- Test all controls and gauges for proper operation.
- Check the ROPS structure for damages.
- Test the cabin lifting function.
7. Attachments
- Inspect all attachments for wear, damage, or missing parts.
- Verify proper functioning of any additional features or accessories.
8. Fluid levels
- Check engine oil, transmission fluid and other fluid levels.
- Ensure that all fluid levels are within the manufacturer’s recommended range.
9. Functional test
- Drive forwards and backwards and test whether the machine is running smoothly.
- Perform load testing to ensure the material handler can handle its rated capacity safely.
10. Safty items
Verify the functionality of emergency stop buttons and other safety systems.

What is a material handler and what are the key features?
A material handler is a type of heavy equipment or machinery designed for efficiently handling various types of materials in industries such as construction, recycling, and manufacturing. These machines are equipped with specific attachments or features to move, lift, and manipulate materials in a controlled and productive manner. The primary purpose of a material handler is to streamline material handling processes and improve operational efficiency. Here are some key characteristics and uses of material handlers:
Material handlers can be equipped with a variety of attachments such as grapples, magnets, clamshells, buckets, and forks. The choice of attachment depends on the specific materials being handled. Material handlers are often used in recycling facilities to sort and load materials such as scrap metal, paper, plastic, and wood. The versatility of attachments allows them to handle different types of materials. Material handlers play a crucial role in waste management operations, handling various types of waste materials in landfills or recycling centers. Material handlers are commonly used in ports and harbors for loading and unloading cargo containers, managing bulk cargo, and transferring goods between ships and storage areas.
Liste de contrôle pour une tombereau articulé
Tu trouveras ici un exemple de liste de contrôle pour une tombereau articulé. Cette fiche d’inspection est utilisée pour inspecter les machines d’occasion. 60 points sont contrôlés et l’inspecteur note toutes ses observations et décrit les défauts constatés. Tu trouveras une liste de tous les formulaires disponibles ICI. La version de la liste de contrôle présentée ici n’est pas la version la plus récente. Nos rapports d’inspection sont régulièrement mis à jour.

