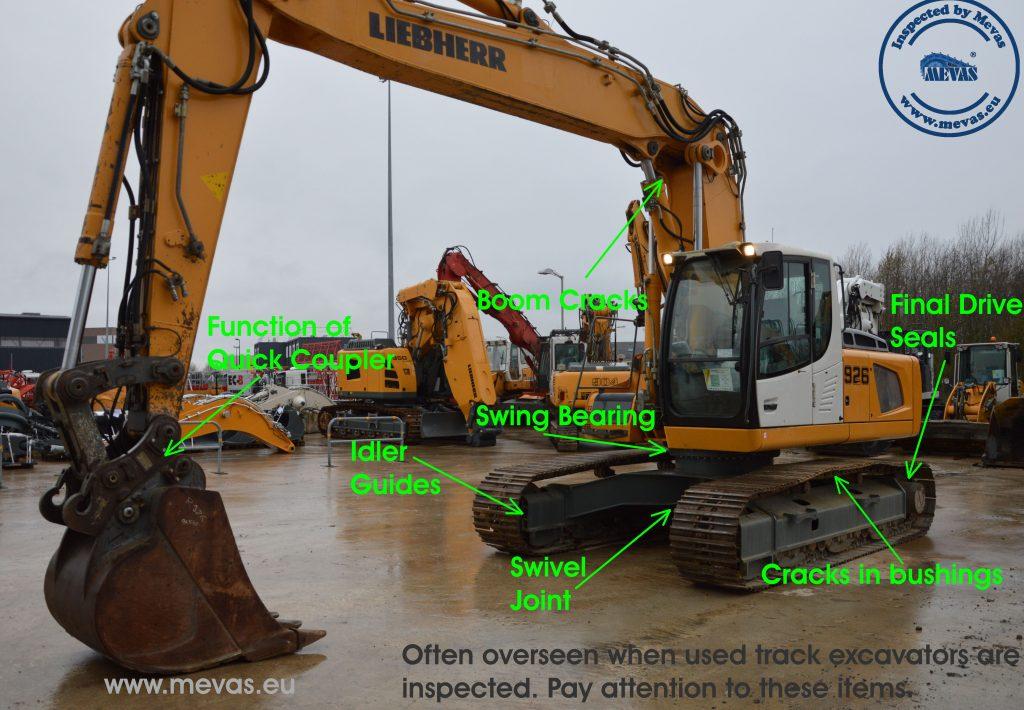
Before you buy a used wheel loader, you should check and test the machine. Here are the key items that should be checked during the inspection of a used wheel loader prior to purchase:
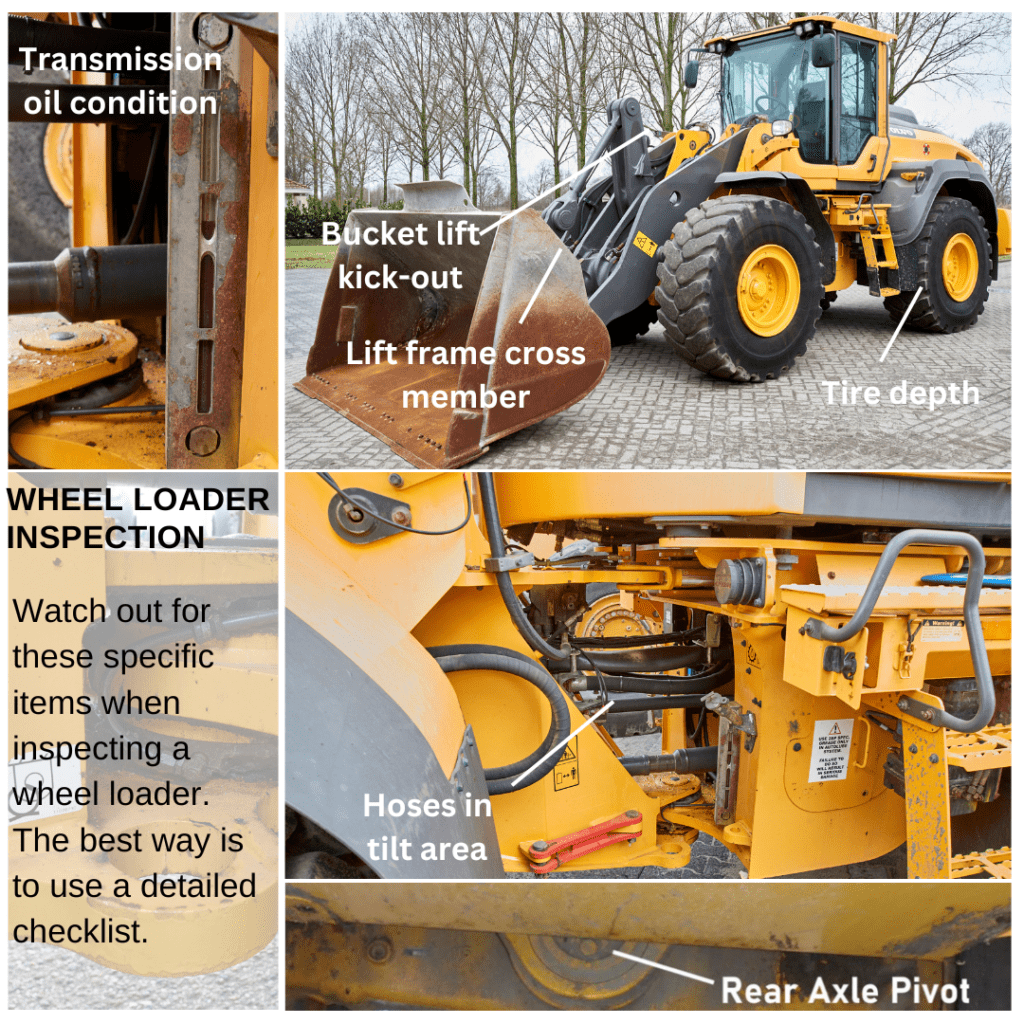
Certainly! Here’s a detailed checklist of items to inspect when considering the purchase of a used wheel loader:
Wheel Loader Inspection Checklist
1. General Appearance
- Look for cracks, dents, excessive rust, or signs of repaired damage.
- Examine the overall cleanliness and maintenance status.
2. Engine
- Start the engine and check for unusual noises, smoke, or vibrations.
- Inspect for leaks around the engine (oil, coolant, fuel).
- Review the air filter and belts for wear.
- Check engine oil quality and level.
3. Transmission & Powertrain
- Test all gears and directions for smooth shifting.
- Listen for abnormal sounds while operating.
- Inspect transmission fluid for correct level and color.
4. Hydraulic System
- Operate all functions (lift, tilt, steering, etc.) and watch for smooth operation.
- Inspect hoses, fittings, and cylinders for leaks or damage.
- Check fluid levels and inspect for contamination.
5. Bucket & Attachments
- Look for wear, cracks, bends, or damaged edges/teeth.
- Check for excessive play in linkages and pivot points.
- Test all attachment movements for precision.
6. Tires & Wheels
- Inspect tread depth, overall wear, and signs of damage (cuts, bulges).
- Check tire pressure.
- Examine wheel rims and lugs for damage or looseness.
7. Brakes
- Test brake function and pedal response.
- Inspect brake pads/shoes, discs/drums for wear.
- Look for leaks or damage in brake lines.
8. Steering & Articulation
- Check steering for smoothness and responsiveness.
- Inspect articulation joints, steering cylinders, and related connections for excessive play, cracks, or lack of lubrication.
9. Operator Cab & Controls
- Examine seat, seatbelt, windows, mirrors, and controls for condition and proper function.
- Test air conditioning, heater, wipers, lights, gauges, and backup alarm.
- Check for water leaks or excessive dust.
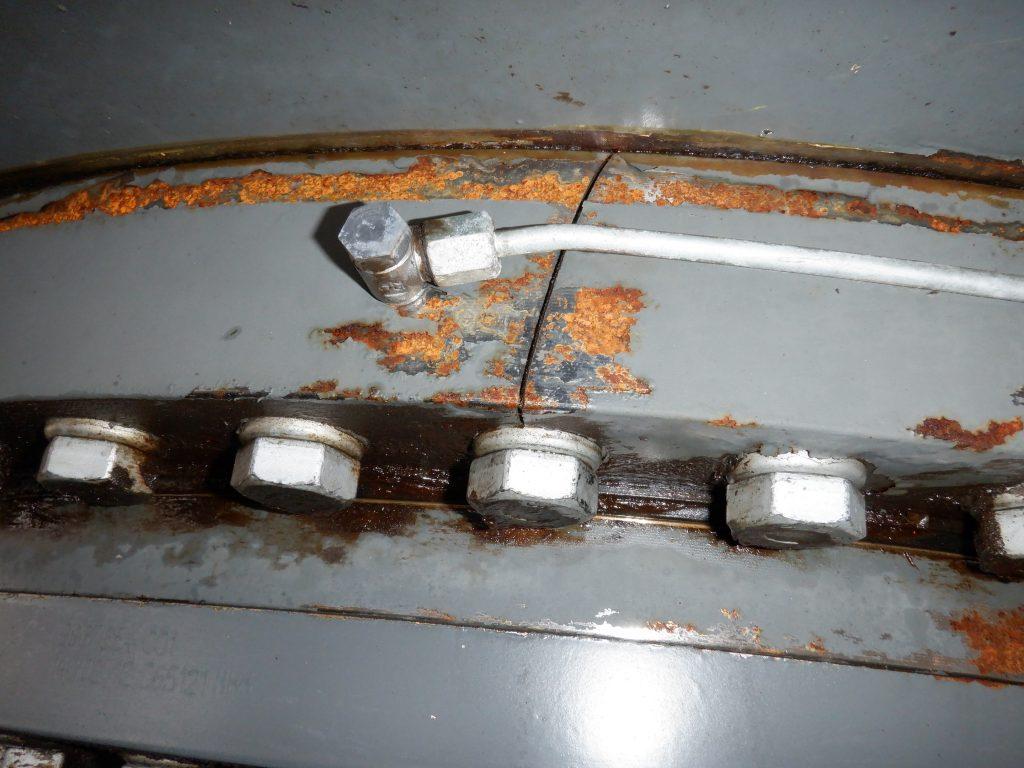
10. Electrical System
- Inspect battery condition and terminals.
- Test all switches, indicators, and lights.
- Check for loose or frayed wires.
11. Fluids & Lubrication
- Check engine oil, hydraulic fluid, coolant, and transmission oil for level and condition.
- Look for signs of neglect or contamination.
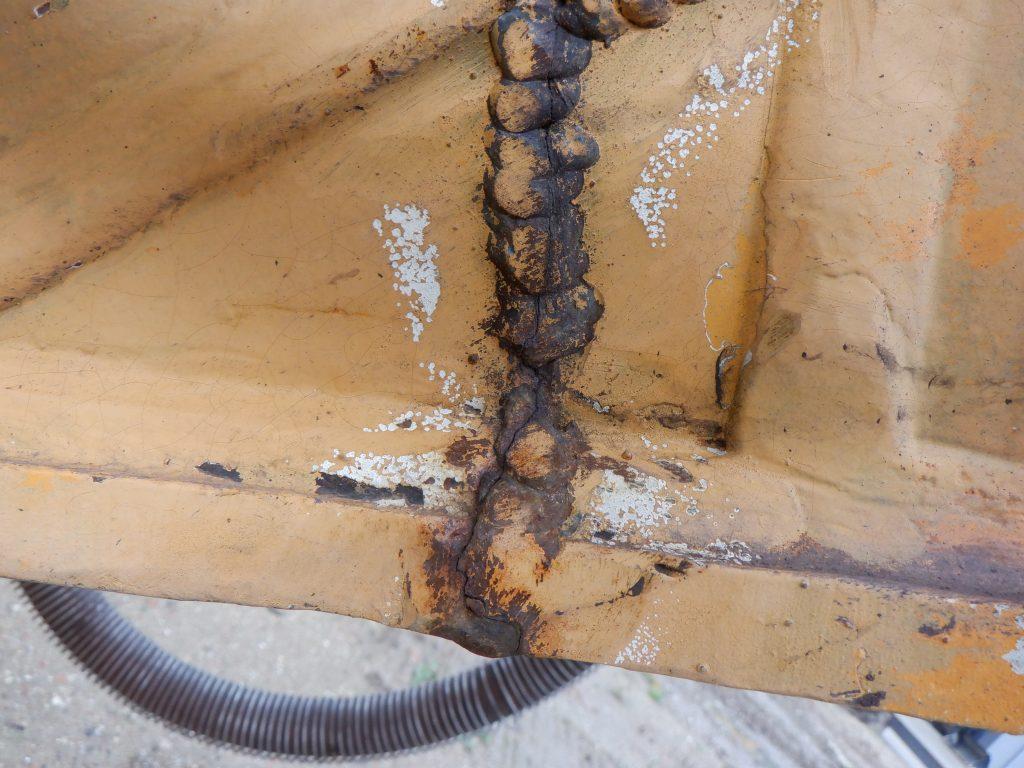
12. Frame & Structure
- Inspect frame and arms for cracks, welds, or signs of previous repairs.
- Check roll-over protection and structural integrity.
13. Documentation
- Request maintenance records and prior inspection/service history.
- Verify serial number and match against documents.
14. Functional & Operational Test
- Perform a driving test to check overall operation.
- Assess loader performance under different loads, paying attention to handling and responsiveness.
Conducting a thorough inspection using these checkpoints will help you gauge the loader’s condition and value, minimizing risks with your purchase.
20 Years of Experience with inspections
Since we have been doing nothing but assessing the condition of used machines for our customers for over 20 years, we know wheel loaders very well. With Volvo and Caterpillar machines, for example, we can read out the ECM and thus obtain data on the machine history and we know the weak points of some series. Asl Mevas if you need a wheel loader inspected anywhere in the world.